When a user searches for information online using Google’s Search Engine, different advertisers battle it out to show their Ads on Google’s Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). But, given the limited advertising space, how does Google decide which advertisers’ ads to show on the page?
Google Search Ads represent a significant part of the digital advertising landscape. And brands today understand more and more the importance of being present in the SERPs when users look for information online. According to Statista, the total Ad Spend in the Search Advertising segment is projected to reach US$260.00bn by the end 2022 and is expected to grow annually by 10.85% to US$435.20bn worldwide by 2027.
It is clearly important for digital marketers to understand how Google Ads and its Ad Rank system works to effectively manage Google Search campaigns and to be critical of the information around them.
So, how does it all work with Google Ads?
Google Search Ads relies upon an auction system where each advertiser bids money to show their advert for specific searches each time a relevant search is made by a user triggering specific keywords. Each time a user makes a search, a new auction among advertisers is initiated.
However, unlike a traditional auction system, it is not strictly the highest bidder that wins the auction and is shown first in the page’s results.
While the monetary bid of an advertiser has its part to play in the auction, Google considers other quality-related factors too in order to determine which advertisers will show up for a user's search.
This is done to ensure that the most relevant ads are shown to the user (and not just the advertisers willing to pay the most money). And this is where Ad Rank comes in.
During each auction, Google looks at multiple factors to determine the advertisers that will be shown on the Search Engine Results Page. Among these factors are:
- The Advertiser’s Maximum Bid
- The Quality of the Advertiser’s Ad
- The Expected Impact of an Advertisers Ad Extensions / Formats
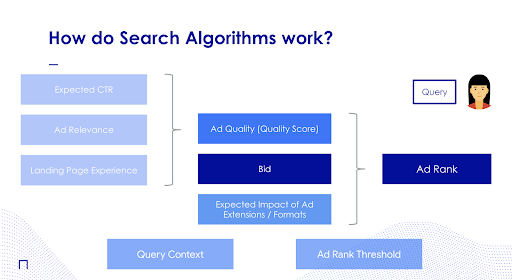
Based on these several factors, each advertiser receives a total score (called their Ad Rank) that determines if their ad will be shown in the user’s Search results or not.
In other words, Ad Rank is essentially the final score that each advertiser receives at the end of the auction based on their Bid, their Quality Score and their use of Ad Extensions in their Ads and the other factors that Google takes into consideration during each auction.
The advertiser with the highest Ad Rank score will have their ads shown highest up in the search results page. Advertisers with lower scores will have their ads shown lower down on the page or not at all.
Let’s look at the different factors in more detail.
The Advertiser’s Maximum Bid
A first factor that Google Ads looks at is the maximum amount of money that a user is willing to pay (or bid) for a user to click on their ad.
For each user’s search, the Ad auction takes place and each advertiser puts forward their maximum bid that they are willing to pay (say for example, 1.20€) to show their ad for the user's search query.
The maximum bid can be set manually by the advertiser with manual bid strategies where the advertiser indicates the maximum amount they are willing to pay for a click. Alternatively, maximum bids can be set automatically for the advertiser by Google for each auction using Automated Bid Strategies. If Automated Bid Strategies are selected, Google's Algorithm will select the most appropriate bid for each auction using vast amounts of data that it has at its disposal to optimise the advertisers bid at each different auction to get the best results.
The Quality of an Advertiser’s Ad (Quality Score)
Google Ads also attributes a Quality Score to each advertiser during the auction to score the estimated usefulness of each Advertiser’s ad to the user. Quality Score is made up of three factors:
- Ad Relevance: how well the advertiser’s advert text matches the users search keyword.
- Expected Clickthrough Rate: how often an advertiser’s ad will be clicked by the user when shown, based on historical search data that Google has.
- Landing Page Experience: how well the advertiser’s landing page will help users find what they are looking for. This considers the landing pages ease of navigability, page loading time, and the relevance and originality of the page’s content.
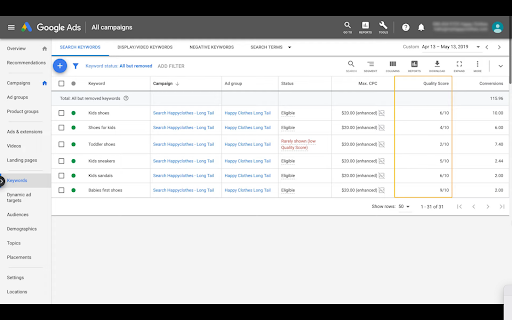
Quality Score is represented on a scale of 1-10, with 1 being the lowest and 10 being the highest. You can find your Quality Score at keyword-level inside your Google Ads campaign. This is because your Ad and landing page are triggered by a specific keyword that you are bidding on based on the user’s search.
The Expected Impact of an Advertisers Ad Extensions / Formats
Advertisers are also able to add additional information to their Ads, called ad extensions, such as, for example, links to other useful pages on their website, a company phone number and information about unique offers. These ad extensions increase the visibility of an advertiser's ad and provide additional relevant information to the user. Google Ads also considers the expected impact of the Advertisers extensions and ad formats to determine the advertiser’s Ad Rank.
Calculating Ad Rank
So, we know more about some of the factors make up an Advertisers Ad Rank. But how is Ad Rank actually calculated?
All of the exact factors making up Ad Rank are not disclosed by Google. However, the Advertiser’s Maximum Bid and their Quality Score, as well as several other factors which Google has access to are used in combination with each other to determine an advertiser’s Ad Rank. For example, if Ad Extensions are also being used, Google’s auction Algorithm will also consider the impact of the Ad Extensions to determine the advertiser’s Ad Rank. Ultimately, the Advertiser with the highest Ad Rank will be shown in first position.
Below is a simplified example, explaining how Ad Rank is calculated for different advertisers (taking into account only Maximum Bid and Quality Score, and not the various other factors which also impact Ad Rank, in this simplified case).
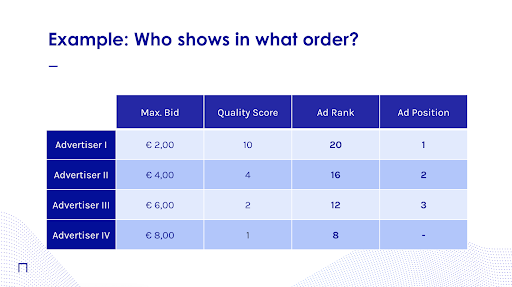
Advertiser 1 has a Maximum bid of €2.00 and a Quality Score of 10/10. Hence, Advertiser 1’s Ad Rank will be 20. This is the highest Ad Rank among all the advertisers in the auction and so the Ads of Advertiser 1 will be shown in first position at the top of the Search Engine’s Results Page.
Conversely, Advertiser 4, has a Maximum bid of €8.00 and a Quality Score of 1/10. This is the lowest Ad Rank among all the advertisers in the auction and their Ads will not be shown at all in the Search Engine’s Results Page due to the limited available Ad Space on the page.
Notice how Advertiser 4 has the highest maximum bid out of all the advertisers in the auction. This example clearly shows how having the highest bids does not guarantee that an advertiser’s ads will be shown first. And higher Quality Scores generally lead to lower cost and improved ad positions to motivate advertisers to create high quality ads.
Wrapping Up
We covered how the Google Ads Auction works and which factors affect an Advertiser’s Ad Rank. We also looked at the specific details of several factors affecting Ad Rank and how Ad Rank is calculated. Improving the Ad Rank of your ads is a continuous process that tests your copywriting skills, your choice of keywords, your budget and bids and the performance of your website. But understanding how the Google Ads auction system works will help you make more informed decisions and ultimately, help you achieve better results for your Google Search campaigns.



